-
[Kalman filter] code, exampleMathematics 2020. 9. 10. 17:22
아래 예제는 https://pinkwink.kr/781 와 유사합니다.
아래 KalmanFilter class 코드는 https://github.com/zziz/kalman-filter 에서 약간의 수정을 하였습니다.
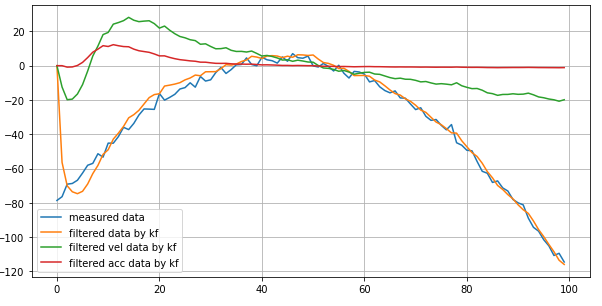
import numpy as np class KalmanFilter(object): def __init__(self, F = None, B = None, H = None, Q = None, R = None, P = None, x0 = None): """ F(=A) [nxn]: system matrix that releates the state at k-1 to the state at step k B [nx1]: it relates the control input(u_k) to the state(x_k) H [mxn]: matrix that relates the state to the measurement Q: process noise covariance. It represents the uncertainty in the process or model R: measurement noise covariance. It represents the unvertainty in the measurement P: error covariance. x0: initial state """ if(F is None or H is None): raise ValueError("Set proper system dynamics.") self.n = F.shape[1] self.m = H.shape[1] self.F = F self.H = H self.B = 0 if B is None else B self.Q = np.eye(self.n) if Q is None else Q self.R = np.eye(self.n) if R is None else R self.P = np.eye(self.n) if P is None else P self.x = np.zeros((self.n, 1)) if x0 is None else x0 def predict(self, u = 0): self.x = np.dot(self.F, self.x) + np.dot(self.B, u) self.P = np.dot(np.dot(self.F, self.P), self.F.T) + self.Q return self.x def update(self, z): y = z - np.dot(self.H, self.x) S = self.R + np.dot(self.H, np.dot(self.P, self.H.T)) K = np.dot(np.dot(self.P, self.H.T), np.linalg.inv(S)) self.x = self.x + np.dot(K, y) I = np.eye(self.n) self.P = np.dot(np.dot(I - np.dot(K, self.H), self.P), (I - np.dot(K, self.H)).T) + np.dot(np.dot(K, self.R), K.T) if __name__ == '__main__': # example import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # get data x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100) measurements = - (x**2 + 2*x - 2) + np.random.normal(0, 2, 100) # params for kalman filter dt = x[1] - x[0] F = np.array([[1, dt, 0], [0, 1, dt], [0, 0, 1]]) H = np.array([1, 0, 0]).reshape(1, 3) Q = np.array([[0.05, 0.05, 0.0], [0.05, 0.05, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]]) R = np.array([0.5]).reshape(1, 1) # define kf kf = KalmanFilter(F = F, H = H, Q = Q, R = R) # predict predictions = [] for z in measurements: predictions.append( kf.predict().ravel() ) kf.update(z) predictions = np.array(predictions) # plot plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.plot(measurements, label = 'measured data') plt.plot(predictions[:, 0], label = 'filtered data by kf') plt.plot(predictions[:, 1], label = 'filtered vel data by kf') plt.plot(predictions[:, 2], label = 'filtered acc data by kf') plt.legend() plt.grid() plt.show()output:
'Mathematics' 카테고리의 다른 글
Fuzzy System - tutorial.pdf, code (0) 2020.09.10 iterative mean, std (standard deviation) (0) 2020.09.10 Global to Local coordinate, Local to Global coordinate (0) 2020.09.10